The modern automobile is a marvel of engineering, comprising various intricate components that work together seamlessly to provide efficient and reliable transportation. In this detailed exploration, we will delve into the five main parts that form the backbone of every car, understanding their functions and significance.
5 Main Parts of a Car
Engine: The Heart of the Car
The engine is undoubtedly the most critical component of any automobile. It serves as the powerhouse, converting fuel into mechanical energy to propel the vehicle forward. Modern cars predominantly feature internal combustion engines, which burn a mixture of fuel and air to produce controlled explosions, driving the pistons and ultimately turning the crankshaft. This rotational motion is then transferred to the wheels, propelling the car forward.
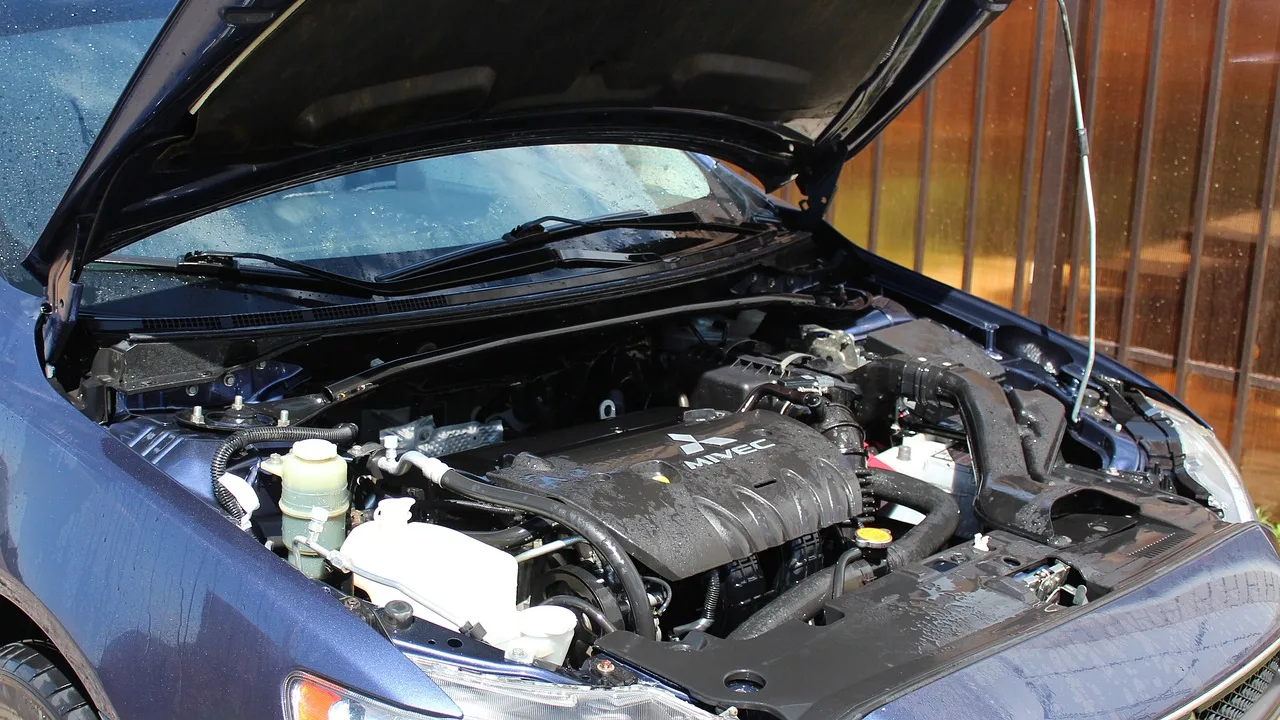

Gasoline engines use a spark plug to ignite the fuel-air mixture, while diesel engines rely on compression ignition. Additionally, the automotive industry has witnessed a surge in electric vehicles (EVs) in recent years, featuring electric motors powered by rechargeable batteries. This shift highlights the evolving landscape of automotive technology and the growing emphasis on sustainability.
- Audi GT50 Concept: A Loud Reminder of Why Car Enthusiasts Fell in Love With Audi
- Nearly 30% of UK Drivers Believe Car Tax Should Be Based on Mileage — Survey
- Why Planes and Boats Escaped the Luxury Tax But Cars Didn’t
- Australia’s Headlight Confusion: Authorities Warn Drivers After Viral $250 Headlight Rule Goes Wild Online
- 2025 Hyundai Venue Facelift Launched in India – Full Details, Variants, and Price
Transmission System: Channeling Power to the Wheels
The transmission system plays a pivotal role in regulating the power generated by the engine and delivering it to the wheels. It ensures optimal performance and efficiency by allowing the driver to control the vehicle’s speed and direction.
There are two primary types of transmissions: manual and automatic. Manual transmissions require the driver to manually shift gears using a clutch and gear lever, providing a greater sense of control. On the other hand, automatic transmissions operate without manual intervention, automatically selecting the appropriate gear ratio based on the driving conditions.

Additionally, modern advancements have led to variable transmissions (CVTs) and semi-automatic transmissions. CVTs offer a seamless range of gear ratios, enhancing fuel efficiency with semi-automatic transmissions provide a compromise between manual and automatic systems, allowing the driver to manually shift gears without operating a clutch.
Chassis: The Structural Framework
The chassis serves as the skeletal framework that supports and connects all the major components of a car. It provides structural integrity, ensuring the vehicle remains stable and secure during operation. The chassis includes the frame, suspension system, and other structural elements to the car’s overall stability and handling.
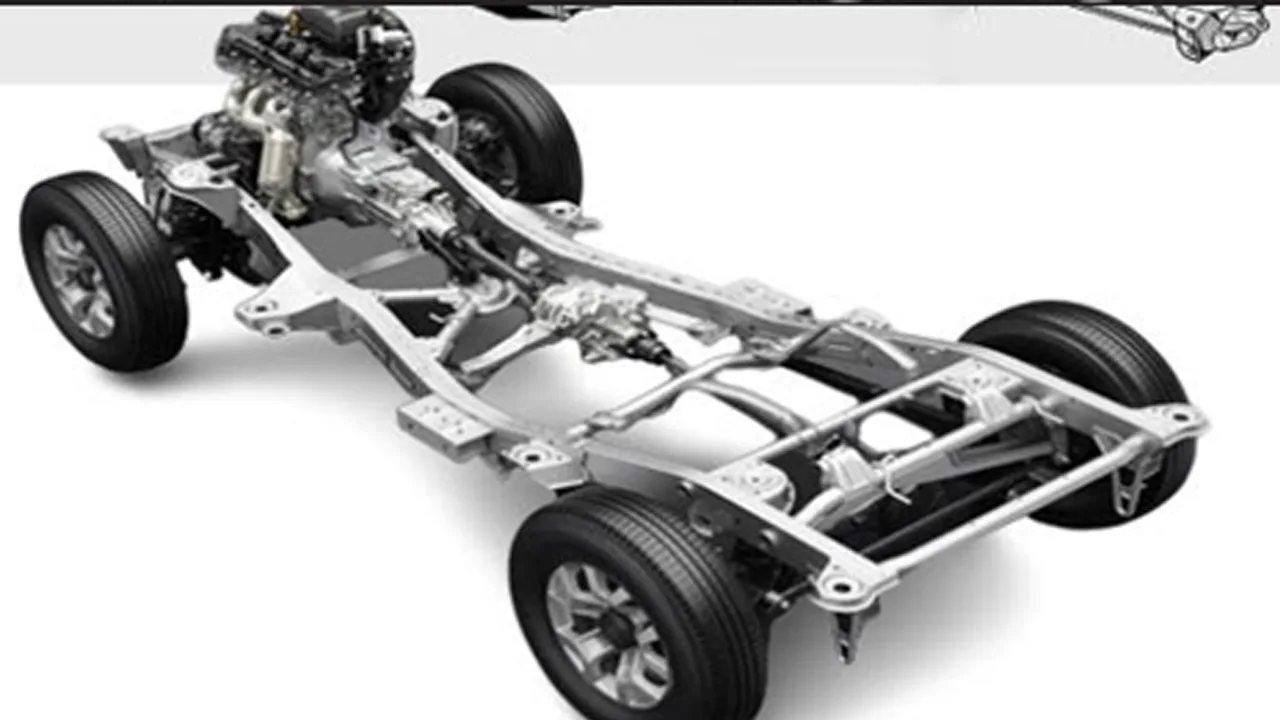

The frame is the main structural component, typically made of steel or aluminum, providing a rigid structure that supports the weight of the vehicle and its occupants. The suspension system, comprising springs, shock absorbers, and other components, maintains contact between the tires and the road surface, contributing to a smooth and controlled ride.
The chassis design varies across vehicles, such as sedans, SUVs, and trucks, to accommodate their specific load-carrying capacities and intended applications.
Electrical System: Powering Innovation and Convenience
The electrical system in a car is a complex network of components that facilitate various functions, from starting the engine to powering electronic accessories. The components include the battery, alternator, starter motor sensors, and wiring.
The alternator, driven by the engine, recharges the battery while the vehicle is in motion, ensuring a continuous power supply.
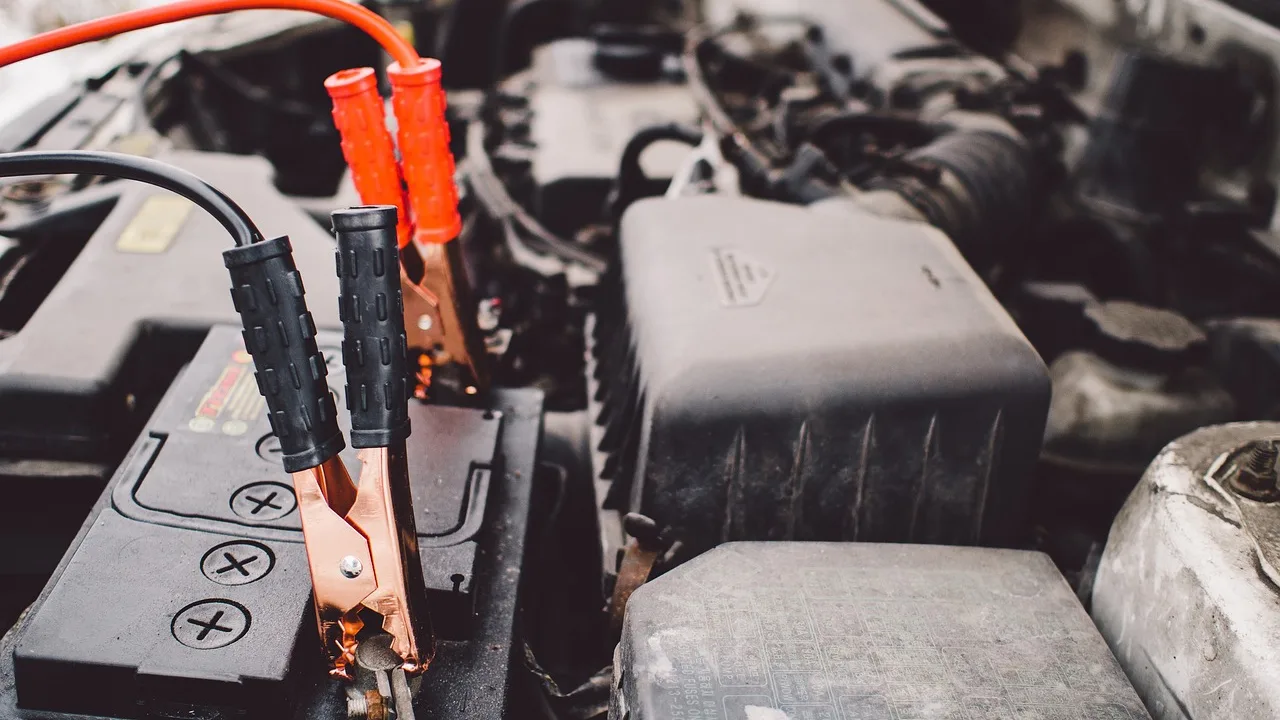

The starter motor initiates the engine’s combustion process by turning the crankshaft, allowing the fuel-air mixture to ignite. Additionally, sensors throughout the car monitor various parameters, such as engine temperature, speed, and emissions, providing data to the engine control unit (ECU) to optimize performance and fuel efficiency.
The electrical system extends beyond essential functions, encompassing entertainment systems, climate control, lighting, and advanced safety features. With the integration of advanced technologies, such as infotainment and driver-assistance systems, the electrical system has become a hub of innovation, enhancing driving experience and safety.
Braking System: Ensuring Safety and Control
The braking system is a critical safety component that allows the driver to control the vehicle’s speed and bring it to a stop when necessary. It has various elements, including the brake pedal, master cylinder, brake lines, brake calipers, brake pads, and brake rotors.
Modern cars typically feature disc brakes, where brake pads clamp onto rotating discs (rotors) attached to the wheel hubs. Some vehicles also incorporate drum brakes, where brake shoes press against the interior surface of a drum. Disc brakes are more common in front-wheel braking systems due to their superior heat dissipation, while drum brakes in the rear.
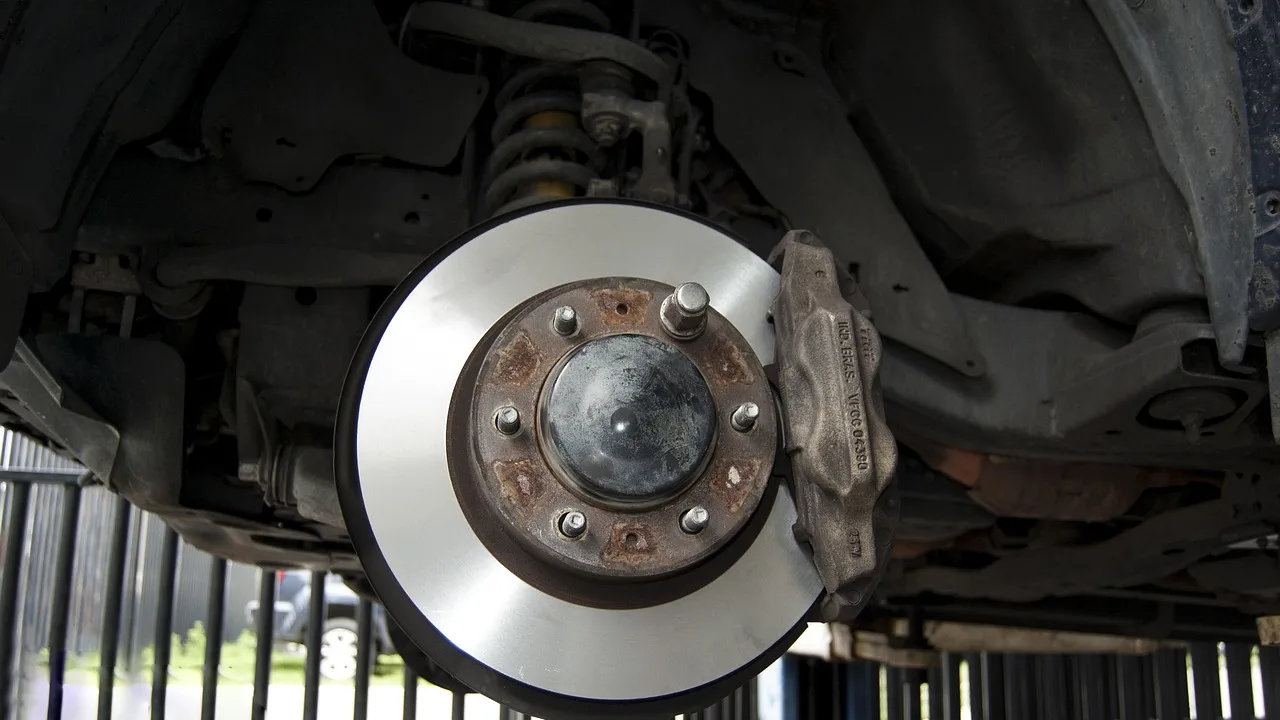

Advanced braking systems include anti-lock braking systems (ABS), electronic brake-force distribution (EBD), and electronic stability control (ESC), enhancing safety by preventing wheel lockup and optimizing brake force distribution.