The design process of iconic American cars is a captivating journey that blends artistry, engineering precision, and cultural resonance. These vehicles are not just modes of transportation; they are symbols of innovation and craftsmanship that have defined eras and left an indelible mark on automotive history.
The design process of iconic American cars explained
Conceptualization:
The journey begins with conceptualization, a phase where designers and engineers collaborate to envision a car that aligns with market trends and reflects the brand’s identity. This stage involves a deep dive into market research, trend analysis, and consumer preferences. Understanding the cultural zeitgeist is paramount, as iconic American cars often encapsulate the spirit of their time.
Market Research and Trend Analysis:
This crucial step involves an in-depth analysis of current market trends, consumer behavior, and emerging technologies. Design teams scour industry reports, conduct surveys, and engage in ethnographic research to gain insights into the evolving automotive landscape. The goal is to identify key features and design elements that resonate with potential buyers.
Ideation and Brand Alignment:
Ideation sessions bring together designers and brand strategists to brainstorm concepts that align with the brand’s values and vision. These early ideation sessions set the foundation for the design direction and help establish a narrative for the upcoming iconic vehicle.
Sketching and Rendering:
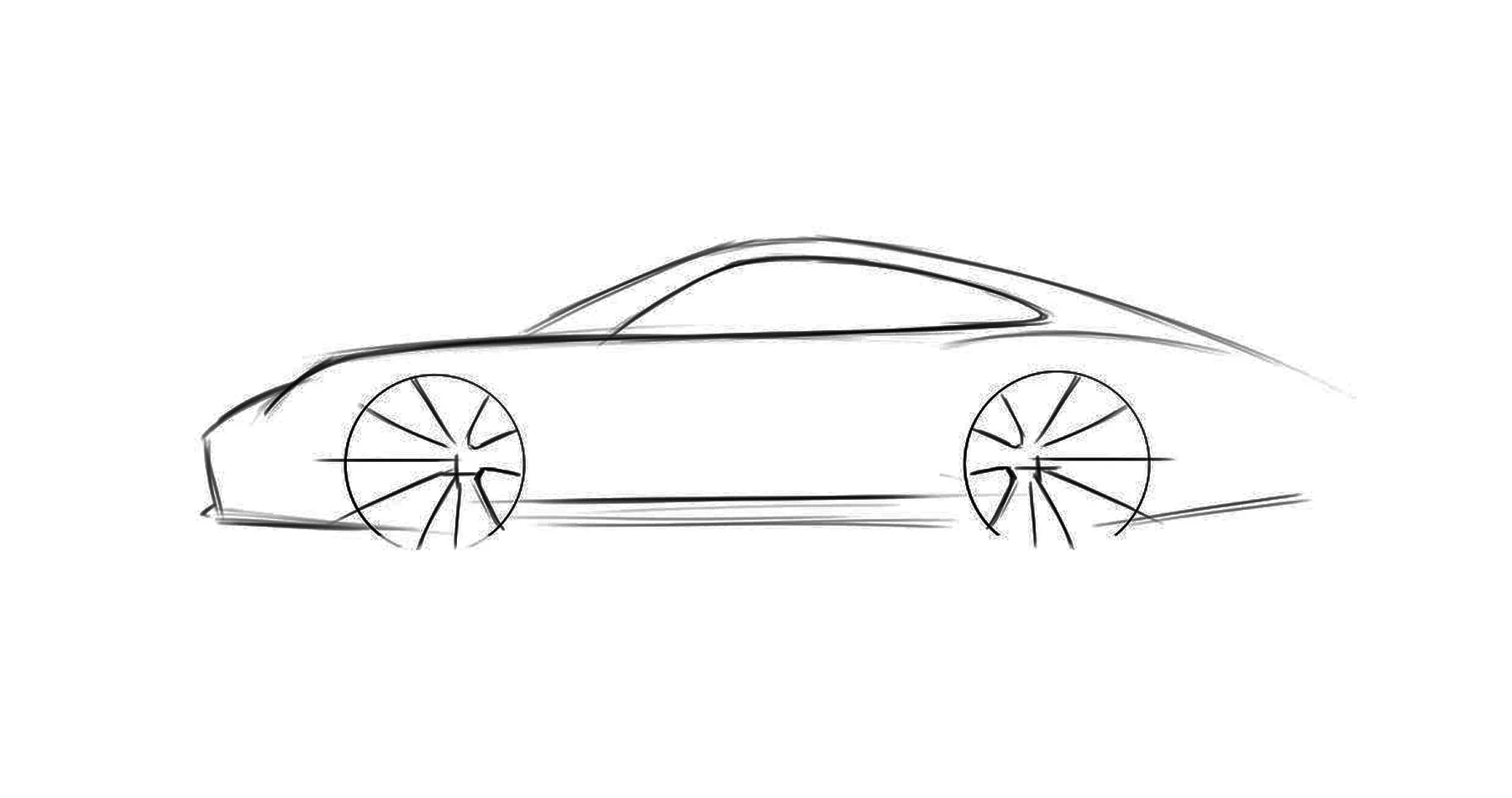
With a conceptual framework, artists and designers transition to the sketching and rendering phase. This stage allows ideas into tangible visual representations, exploring various design options and aesthetics.
Initial Sketches:
Designers put pen to paper or stylus to tablet, sketching preliminary concepts that capture the essence of the envisioned car. These sketches serve as a starting point for further exploration, capturing the initial vision in broad strokes.
Digital Rendering:
As technology advances, digital tools become integral to the design process. Designers use Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software to create digital renderings that provide a more nuanced and detailed representation of the envisioned vehicle. Digital rendering allows for easier collaboration and iteration as designs evolve.

Clay Modeling:
This hands-on approach allows designers to assess proportions, lines, and surfaces with a tangible, physical representation of the car.
Physical Representation:
Skilled artisans use clay to sculpt a scale model of the car based on digital designs. This process provides a tactile experience for designers, enabling them to evaluate the design from different angles and perspectives. Adjustments and refinements are made based on the feedback generated during this phase.
Feedback and Iteration:
Clay models undergo scrutiny from the design team and, in some cases, key stakeholders. Feedback is collected to identify areas for improvement or adjustment. Iterative cycles of modeling and refinement continue until the team achieves a consensus on the final design direction.
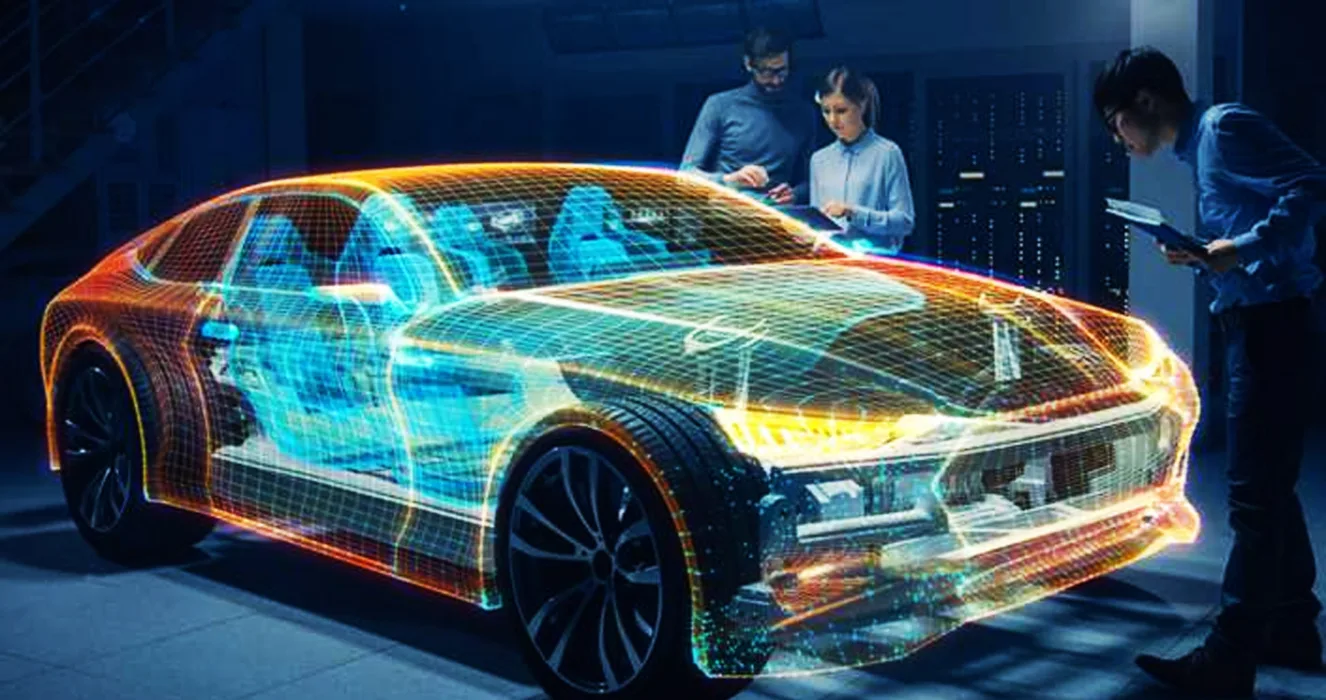
Digital Prototyping:
Advancements in technology have revolutionized the design process, and digital prototyping has become a pivotal phase in crafting iconic American cars.
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) Integration:
The digital prototype is developed through sophisticated CAD software, incorporating intricate details. This phase facilitates seamless integration between design and engineering, ensuring aesthetic vision aligns with the vehicle’s performance capabilities.
Simulation and Analysis:
Digital prototypes undergo rigorous simulation and analysis. Engineers assess factors such as aerodynamics, structural integrity, and weight distribution. Virtual tests simulate real-world scenarios, providing valuable insights into the car’s potential performance and identifying areas for optimization.
Engineering Integration:
As the design gains momentum, it’s time for the critical integration of mechanical and technical components. Collaboration between design and engineering teams intensifies to ensure a harmonious balance between form and function.
Collaborative Approach:
Designers and engineers work closely to integrate the design with the mechanical and technical aspects of the vehicle.
Performance Optimization:
Fine-tuning occurs to enhance the car’s performance capabilities. It involves iterative adjustments to the design, incorporating feedback from engineering assessments. The goal is to achieve optimal performance without compromising the aesthetic integrity of the vehicle.
Material Selection:
Choosing the materials is a pivotal aspect of car design. Material selection influences factors such as weight, durability, and overall aesthetics. Iconic American cars often feature innovative materials to enhance performance and visual appeal.
Prototyping and Testing:
Physical prototypes are undergoing rigorous testing now that the engineering and design features. In this phase, the car meets or exceeds industry for performance, safety, and reliability.
Styling Refinement:
With feedback from testing, the design undergoes further refinement. Stylistic elements such as headlights, grilles, and wheel designs enhance visual appeal while maintaining functionality.
Finalization and Production Planning:
This phase involves detailing specifications for assembly lines, tooling, and quality control measures. Close coordination with suppliers and manufacturers ensures a seamless transition from design to mass production.
Launch and Marketing:
The iconic American car is now ready to debut in the market, marketing activities the vehicle’s distinctions and significance in the history of automobiles.