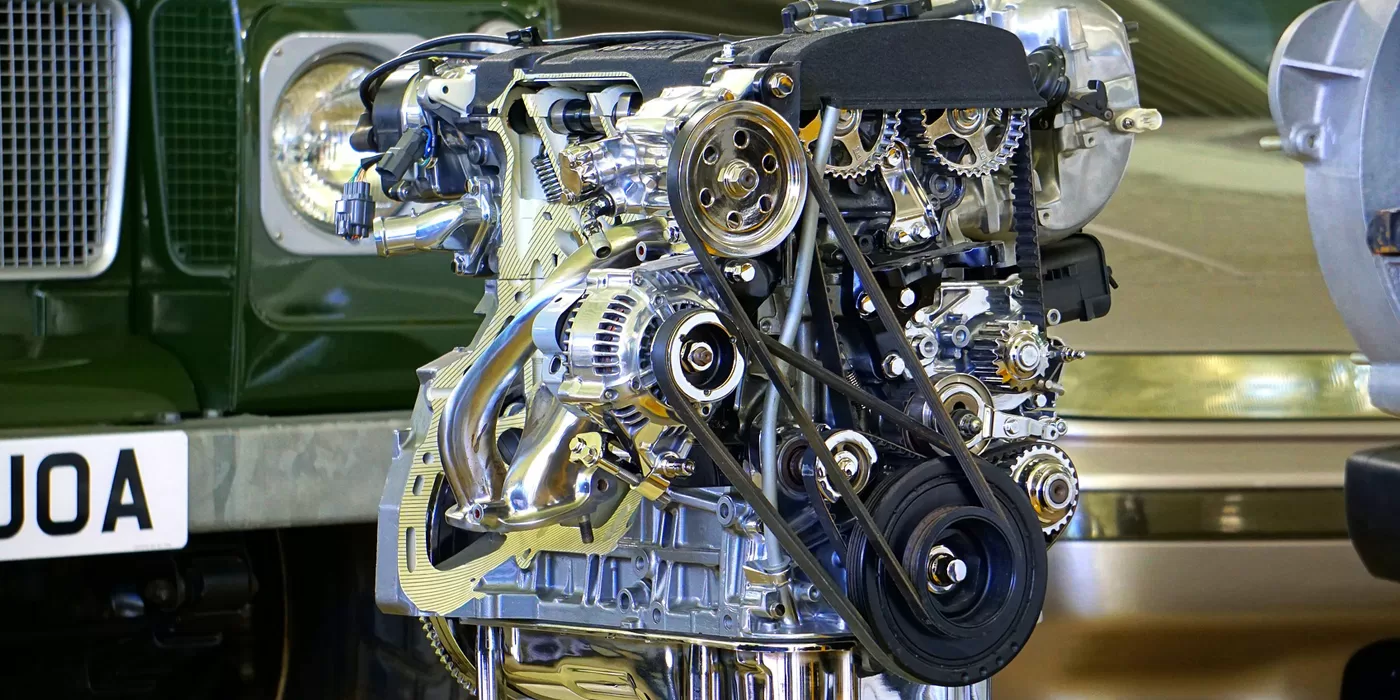
Part of car engine and function- Introduction
An internal combustion engine (ICE) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some parts of the motor.
Usually, rotors, turbine blades, pistons, or nozzles are the objects to which the force acts. The component moves by this force across a distance, turning chemical energy into usable mechanical energy.
Part of car engine and function-Parts of an Internal Combustion Engine:
Cylinder:
The cylinder is a cylindrical metal component that serves as the combustion chamber. It houses the piston, which moves up and down inside the cylinder as the engine runs.
Piston:
The piston is a cylindrical component that moves up and down inside the cylinder. It expands and contracts the air/fuel combination in the cylinder and connects to the crankshaft via a connecting rod.
Crankshaft:
The crankshaft is the main element of the engine that transforms the pistons’ reciprocating action into rotary motion. The crankshaft is connected to the pistons by connecting rods and rotates as the pistons move up and down.
Connecting Rod:
The connecting rod connects the piston to the crankshaft and allows the engine to transfer its motion to the crankshaft.
Camshaft:
The camshaft is a shaft with cam lobes that regulates how the valves open and close. It utilizes to control the timing of the valve actions and revolves in unison with the crankshaft.
Valves:
The valves regulate the flow of fuel and air into the cylinder and the exhaust coming out of the cylinder. The camshaft opens and closes them to let the air/fuel mixture into the cylinder and the exhaust gases out.
Spark Plug:
The spark plug is a device that delivers an electric spark to ignite the air/fuel mixture in the cylinder. It links to the ignition system from the cylinder head. It connects to the ignition system from the cylinder head.
Fuel System:
Delivering fuel from the fuel tank to the engine is the responsibility of the fuel system. It may consist of a fuel pump, fuel injectors, and fuel lines.
Ignition System:
the ignition system is responsible for supplying the spark to ignite the mixture of air and fuel in the cylinder. The ignition system provides the spark to ignite the air/fuel mixture in the cylinder. It may consist of a distributor, spark plugs, and high-tension wires.
Functions of the Parts in an Internal Combustion Engine:
Cylinder:
The cylinder serves as the combustion chamber where the air/fuel mixture is compressed and burned to generate power.
Piston:
The piston moves up and down inside the cylinder and compresses the air/fuel mixture. As the air/fuel mixture ignites and burns, the pressure of the gases generated pushes the piston down, converting the energy from the combustion into mechanical energy.
Crankshaft:
The crankshaft converts the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotary motion. The crankshaft revolves as the pistons rise and fall, supplying the mechanical power required to turn the car’s wheels.
Connecting Rod:
The connecting rod enables the piston to transmit motion to the crankshaft by joining it to the latter.
Camshaft:
The camshaft is responsible for controlling the timing of the valve events.
It is just a general overview of the parts of an engine and their functions. Depending on the type of engine, the producer, and the intended purpose, an engine’s precise design and components can change.